להקשיב ולקרוא
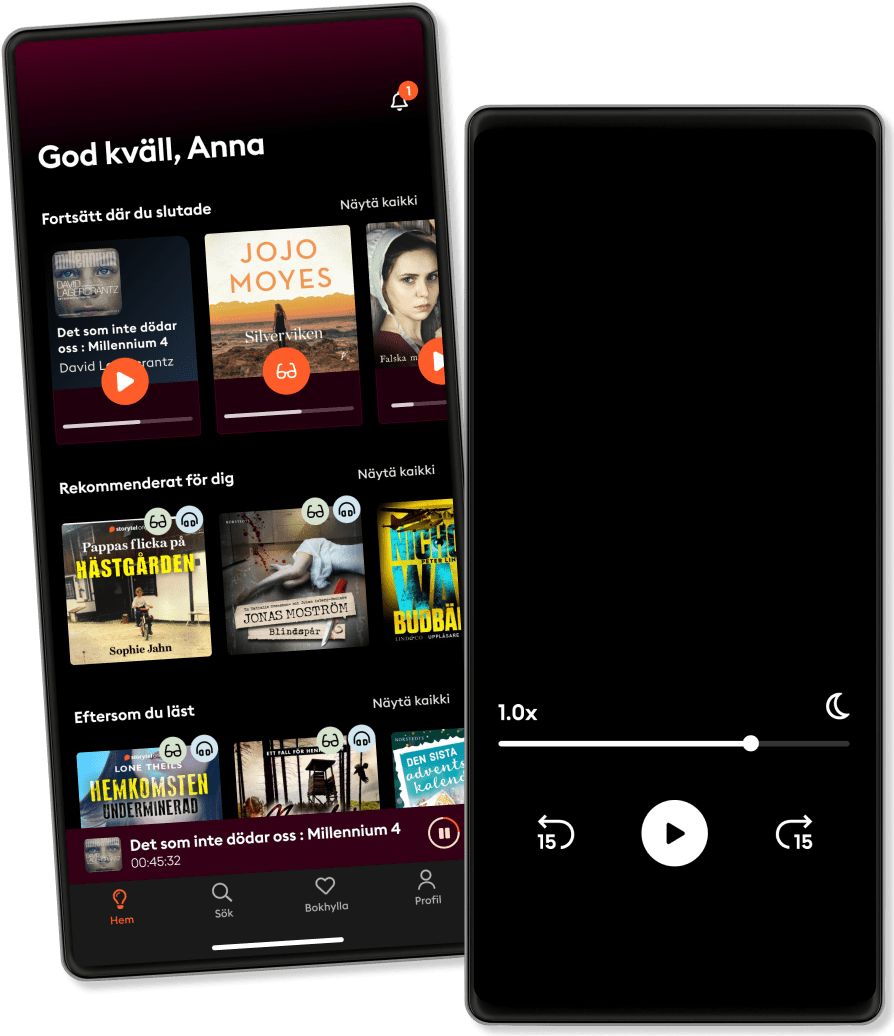
היכנסו לעולם אינסופי של סיפורים
- קראו והקשיבו כמה שאתם רוצים
- למעלה ממיליון כותרים
- ספרים בלעדיים + Storytel Originals
- ניתן לבטל מתי שרוצים
The Great Siege of Malta: The History of the Battle for the Mediterranean Island Between the Ottoman Empire and Knights Hospitaller
- על ידי
- בהשתתפות:
- מוֹצִיא לָאוֹר
After being forced out of Rhodes by the Ottomans in the early 16th century, the Knights Hospitaller spent seven years residing in Sicily without an official home or garrison, but around 1530, Holy Roman Emperor Charles V decided to gift the order the islands of Malta and Gozo, as well as the port city of Tripoli in North Africa, as a fiefdom. The emperor’s motivations varied, but most historians believe he granted the knights the territory partially out of religious devotion and mainly to protect those regions from the looming Ottoman threat. Both Malta and Gozo were between Sicily and the North African coast and were prime locations for the Ottoman Empire to try to make their next move to gain inroads into Europe.
In 1565, the Knights Hospitaller were attacked by Suleiman, who sent 40,000 soldiers to attempt to wrest control of Malta from them. This would become known as the Great Siege of Malta, lasting from May 18-September 11. The first two months of the siege were devastating for the Hospitallers, who lost most of their cities and half of their 8,000 knights. On August 23, the Ottomans launched their last assault upon Malta. The fighting was intense, and even wounded knights participated. The Ottoman army was unable to break through the Order’s fortifications, as the garrison had repaired the worst of the damages and any breakages to avoid giving the Ottomans an advantage. After the Great Siege of Malta, the Knights Hospitaller would have no more decisive victories against their enemies, which should come as no surprise given that by the time the Ottomans left, the order only had 600 men capable of fighting.
© 2020 Charles River Editors (ספר מוקלט ): 9781094279190
תאריך הוצאה
ספר מוקלט : 13 במרץ 2020
אחרים גם נהנו...
- The Siege of Vienna (1529): The History and Legacy of the Decisive Battle that Prevented the Ottoman Empire’s Expansion into Western Europe Charles River Editors
- The Battle of Vienna (1683): The History and Legacy of the Decisive Conflict between the Ottoman Turkish Empire and Holy Roman Empire Charles River Editors
- Medieval Europe Chris Wickham
- The Knights Hospitaller: The History and Legacy of the Medieval Catholic Military Order Charles River Editors
- Arabs: A 3,000-Year History of Peoples, Tribes, and Empires Tim Mackintosh-Smith
- The Great Siege: Malta 1565 Ernle Bradford
- Six Days of War: June 1967 and the Making of the Modern Middle East Michael B. Oren
- A Distant Mirror: The Calamitous 14th Century Barbara W. Tuchman
- The Crusades Abigail Archer
- Powers and Thrones: A New History of the Middle Ages Dan Jones
- ארבע ההסכמות דון מיגל רואיס
4.5
- תיק איה נילי אסיא
4.4
- האיש שאהב את הטלפון שלו יותר מדי יובל אברמוביץ'
4
- הרגלים אטומיים ג'יימס קליר
4.8
- Nexus נקסוּס יובל נח הררי
4.4
- הפריצה: להוביל בתחומך: להוביל בתחומך Yuval Abramovitz
4.5
- משאלה אחת ימינה אשכול נבו
4.7
- כוחו של הרגע הזה אקהרט טול
4.7
- לשרוף את הספינות מתן ניסטור
4.6
- חוק 5 השניות מל רובינס
4.3
- מועדון ה-5 בבוקר רובין שארמה
4.3
- הרפתקאות דוד אריה בערבות רומניה ינץ לוי
4.5
- שלוש קומות אשכול נבו
4.7
- סדר את המיטה שלך אדמירל ויליאם ה. מקרייבן
4.5
- הרפתקאות דוד אריה בג'ונגל הסיבירי ינץ לוי
4.8
איזה מינוי מתאים לך?
מאות אלפי ספרים
מצב ילדים (תוכן שמתאים לקטנטנים)
הורדת ספרים לקריאה והאזנה בלי אינטרנט
אפשר לבטל בכל עת
Unlimited
האזנה וקריאה בלי הגבלה.
חשבון 1
גישה בלתי מוגבלת
האזנה וקריאה בלי הגבלה
קריאה והאזנה גם בלי אינטרנט
אפשר לבטל בכל עת
Family
גלו ספרים לכל המשפחה. היכנסו יחד לתוך עולם של סיפורים.
2 חשבונות
גישה בלתי מוגבלת
שני חשבונות
האזנה וקריאה בלי הגבלה
אפשר לבטל בכל עת
עִברִית
ישראל